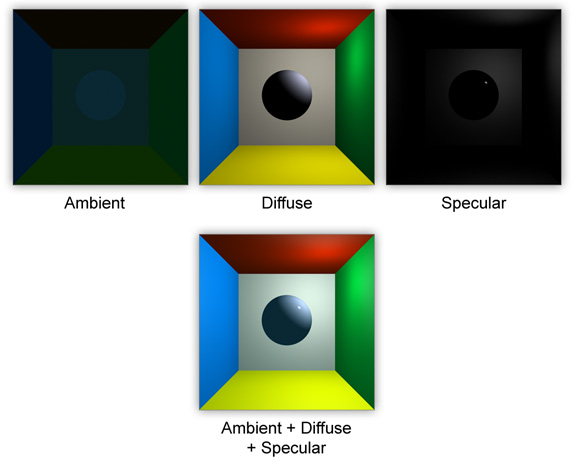
Light Color
Light sources are composed of three of the lighting terms we discussed earlyer: ambient, diffuse and specular. These 3 terms combined make up the final lighting of the geometry. Illustrated in this image:
To set up each of these terms you call GL.Light with a parameter name of LightParameter.Ambient, LightParameter.Diffuse or LightParameter.Specular. Each of these takes a four component float array. The values passed in represent the RGBA color of the specified term. The following code demonstrates:
float[] white = new float[]{1, 1, 1, 1};
float[] blue = new float[]{0, 0, 1, 1};
// Set ambient term blue
GL.Light(LightName.Light0, LightParameter.Ambient, blue);
// Set diffuse term blue
GL.Light(LightName.Light0, LightParameter.Diffuse, blue);
// Set specular term white
GL.Light(LightName.Light0, LightParameter.Specular, white);
The above code and image match. Note how in the image the ambient and diffuse terms are both blue, and the specular term (the highlight) is white. Adding all the terms up produces the final image.
The default value of every term for all lights is black (0, 0, 0, 1) with two exceptions: Light 0 has a default diffuse and specular term of white (1, 1, 1, 1)
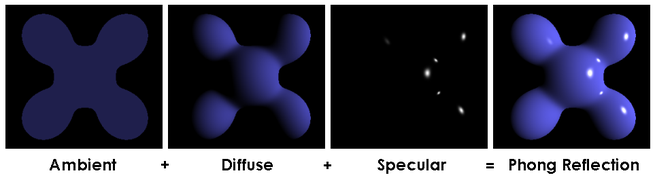
Because this concept is pretty important, here is another image demonstrating it: