Raycast Triangle
Raycsating against a triangle is a simple process
- Create a plane from the 3 points of the triangle
- Raycast against that plane
- Check if the raycast point is inside the triangle
You already have all the fnuctions needed to implement this in a rudimentary way. However, our Point In Triangle test is not optimal! Also, we will have to make a special version of raycast plane!
Barycentric Point In Tirangle
Remember, when we did the point in triangle test, we did not use barycentric coordinates.
It's time to switch that. You can either implement barycentric coordinates straight up in the raycast triangle code, or you can change your point in triangle code and call that. If you change the point in triangle equation, make sure to run the unit test again to ensure everything still works.
Onto implementing barycentric coordinates! Watch this video:
Special Plane Raycast
Next up, the raycast plane function we have will not work. This is because that function takes the planes normal into consideration. I suggest making a new private function:
private static bool RaycastNoNormal(Ray ray, Plane plane, out float t) {
Inside the plane raycast code, we do a dot product of plane normal and ray normal, store the result in nd. We later test if the normals are pointing in the same direction by doing this bit:
if (nd >= 0f) {
t = -1;
return false;
}
Thats where the problem is, the only time we want the ray and the plane to not intercept is when they are parallel, that is when nd is 0. Remember, use an epsilon. This will take the direction of the plane and ray needing to be the same out of the equation.
On Your Own
Add the following function to the Collisions class:
public static bool Raycast(Ray ray, Triangle triangle, out float t) {
// Implement your code here
}
// Conveniance method, returns t without an out param
// If no collision happened, will return -1
public static float Raycast(Ray ray, Triangle triangle) {
float t = -1;
if (!Raycast(ray, triangle, out t)) {
return -1;
}
return t;
}
// Conveniance method, returns the point of intersection
public static bool Raycast(Ray ray, Triangle triangle, out Point p) {
float t = -1;
bool result = Raycast(ray, triangle, out t);
p = new Point(ray.Position.ToVector() + ray.Normal * t);
return result;
}
And provide an implementation for it!
Unit Test
You can Download the samples for this chapter to see if your result looks like the unit test.
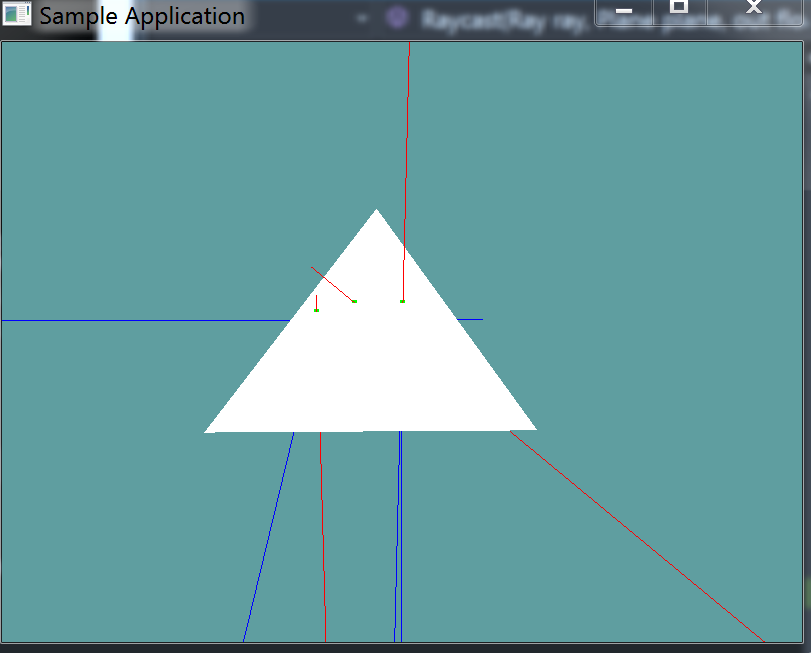
A trianlge and a few rays are rendered. Any ray intersecting the triangle is red. All rays not intersecting the triangle are blue. Green dots are rendered at the points of intersection. The constructor of this unit test will spit out errors if it finds any
using OpenTK.Graphics.OpenGL;
using Math_Implementation;
using CollisionDetectionSelector.Primitives;
namespace CollisionDetectionSelector.Samples {
class RaycastTriangle : Application {
Triangle test = new Triangle( new Point(5.207108f, -1.792894f, -3.949748f),
new Point(5.207108f, -1.792894f, 5.949748f),
new Point(-1.792894f, 5.207108f, 1));
public Ray[] rays = new Ray[] {
new Ray(new Point(0f, 0f, 0f), new Vector3(0f, -1f, 0f)),
new Ray(new Point(0.5f, 0.5f, 0f), new Vector3(-1f, -1f, 0f)),
new Ray(new Point(1f, 1f, 0f), new Vector3(1f, 1f, 0f)),
new Ray(new Point(1f, 1f, -3f), new Vector3(0f, 0f, 1f)),
new Ray(new Point(2f, 2f, 3f), new Vector3(0f, -1f, 0f)),
new Ray(new Point(3f, 3f, 3f), new Vector3(-3f, -3f, -3f)),
new Ray(new Point(1f, 1f, 3f), new Vector3(-2f, -3f, 1f)),
};
public override void Intialize(int width, int height) {
GL.Enable(EnableCap.DepthTest);
GL.PointSize(5f);
GL.PolygonMode(MaterialFace.FrontAndBack, PolygonMode.Fill);
bool[] results = new bool[] {
false, false, true, false, true, true, false
};
float t;
for (int i = 0; i < results.Length; ++i) {
if (Collisions.Raycast(rays[i], test, out t) != results[i]) {
LogError("Expected ray at index: " + i + " to " +
(results[i] ? "intersect" : "not intersect") +
" the triangle");
}
}
}
public override void Render() {
base.Render();
DrawOrigin();
GL.Color3(1f, 1f, 1f);
test.Render();
float t;
foreach (Ray ray in rays) {
if (Collisions.Raycast(ray, test, out t)) {
Point colPoint = new Point();
Collisions.Raycast(ray, test, out colPoint);
GL.Color3(0f, 1f, 0f);
colPoint.Render();
GL.Color3(1f, 0f, 0f);
}
else {
GL.Color3(0f, 0f, 1f);
}
ray.Render();
}
}
private void Log(string s) {
System.Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
}