AABB - Axis Aligned Bounding Box
An AABB (Axis Aligned Bounding Box) is a 3D box. It's width / height / depth don't have to be equal, but the width is always aligned to the X axis, the height to the Y axis and depth to the Z axis. That is to say, this box can't be rotated.
AABB's are pivotal to spacial partitioning, they let us cut a section of 3D space up into smaller sections of 3D space. AABB's also serve as a great acceleration structure for hit detection, but more on that later.
The first question we have to ask is how to represent an AABB? There are two common ways, by storing the leftmost and rightmost corners, OR by storing the center point and a vector of how far the box extends on each side.
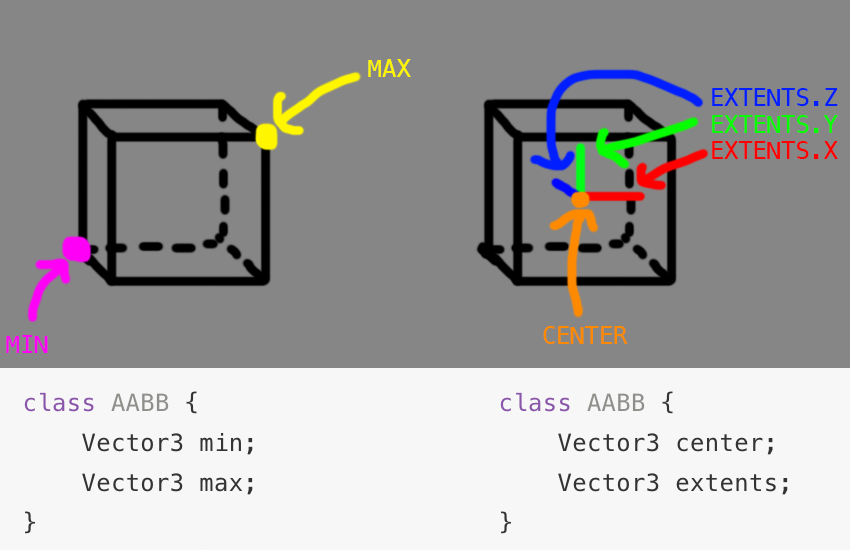
Most mathematical texts describe an AABB as a min and max point. Because of this, i like to design my AABB classes as such. However, there is a bit of a problem, what if a user sets the min.X of the AABB to be greater than the max.X? For this reason i usually include 2 bits of code:
// THIS BLOCK IS JUST SAMPLE CODE, DON'T COPY IT!
public bool IsValid {
get {
return Min.X < Max.X && Min.Y < Max.Y && Min.Z < Max.Z;
}
}
public void Fix() {
if (Min.X > Max.X) {
// SWAP
}
if (Min.Y > Max.Y) {
// Swap
}
if (Min.Z > Max.Z) {
// Swap
}
}
At the end of the day, your representation doesn't matter much. If you represent your AABB as a min and max internally, you can expose getter only Center and Extents properties.
Code Guide
This code guide is actually valid C# code. If you do all the TODO sections, it will compile. Like always, you don't have to use / follow this implementation.
One thing to keep in mind, the constructor that takes a min / max point as argument should call the Fix function because we can't trust user provided values.
That's the only constructor that needs to call Fix, the one that takes a point and extents builds min and max in-line, so you know it will be correct!
using System;
using OpenTK.Graphics.OpenGL;
using Math_Implementation;
namespace CollisionDetectionSelector.Primitives {
class AABB {
public Point Min = new Point();
public Point Max = new Point();
public Point Center {
get {
// FIGURE OUT CENTER POINT
}
// NO SET!
}
public Vector3 Extents {
get {
// FIGURE OUT EXTENTS
}
// NO SET!
}
public bool IsValid {
// TODO: Implement, getter only, no setter!
}
public void Fix() {
// TODO: Implement
}
public AABB() {
// TODO: Make a unit AABB
// Min = -1, max = +1 on all axis
}
public AABB(Point min, Point max) {
// TODO: Set Min and Max
// Don't forget, could be invalid
}
public AABB(Point center, Vector3 extents) {
// TODO: Set Min and Max
}
// No need to change below this, render and to-string
// functions are provided
public void Render() {
GL.Begin(PrimitiveType.Quads);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Max.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Min.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Min.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Max.Z);
GL.Vertex3(Min.X, Max.Y, Min.Z);
GL.End();
}
public override string ToString() {
string result = "Min: (" + Min.X + ", " + Min.Y + ", " + Min.Z + "), ";
result += "Max: ( " + Max.X + ", " + Max.Y + ", " + Max.Z + ")";
return result;
}
}
}
On Your Own
Implement the AABB class. You can use the code guide above, or use your own implementation
Sample / Unit Test
You can Download the samples for this chapter to see if your result looks like the unit test.
The sample will render 3 AABB's constructed using the 3 different constructors above. It will render each AABB, it's min and max points (in magenta and yellow), it's center point (In light blue) and it's extents (r, g, b for x, y, z). If there are any errors, the console should print red. This is what the sample will look like:

using OpenTK.Graphics.OpenGL;
using Math_Implementation;
using CollisionDetectionSelector.Primitives;
namespace CollisionDetectionSelector.Samples {
class AABBSample : Application {
protected Vector3 cameraAngle = new Vector3(120.0f, -10f, 20.0f);
protected float rads = (float)(System.Math.PI / 180.0f);
AABB aabb1 = new AABB();
AABB aabb2 = new AABB(new Point(-3, -2, -3), new Point(-1, -1, -2));
AABB aabb3 = new AABB(new Point(5, 5, 5), new Vector3(2, 4, 3));
public override void Intialize(int width, int height) {
// Seeing the back face of a square gives a better
// overview of the actual geometry
//GL.Enable(EnableCap.CullFace);
GL.PolygonMode(MaterialFace.FrontAndBack, PolygonMode.Line);
GL.PointSize(4f);
System.Console.ResetColor();
CheckAABBMinMax(aabb1, 1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1);
CheckAABBCenterExtents(aabb1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1);
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB1: " + aabb1);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tCenter: " + aabb1.Center);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExtents: " + aabb1.Extents.X + ", " + aabb1.Extents.Y + ", " + aabb1.Extents.Z);
System.Console.ResetColor();
CheckAABBMinMax(aabb2, 2, -3, -2, -3, -1, -1, -2);
CheckAABBCenterExtents(aabb2, 2, -2, -1.5f, -2.5f, 1, 0.5f, 0.5f);
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB2: " + aabb2);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tCenter: " + aabb2.Center);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExtents: " + aabb2.Extents.X + ", " + aabb2.Extents.Y + ", " + aabb2.Extents.Z);
System.Console.ResetColor();
CheckAABBMinMax(aabb3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 7, 9, 8);
CheckAABBCenterExtents(aabb3, 3, 5, 5, 5, 2, 4, 3);
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB3: " + aabb3);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tCenter: " + aabb3.Center);
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExtents: " + aabb3.Extents.X + ", " + aabb3.Extents.Y + ", " + aabb3.Extents.Z);
}
protected void CheckAABBCenterExtents(AABB aabb, int num, float cx, float cy, float cz, float ex, float ey, float ez) {
if (aabb.Center.X != cx || aabb.Center.Y != cy || aabb.Center.Z != cz) {
System.Console.ForegroundColor = System.ConsoleColor.Red;
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB" + num + ", center is wrong");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tGot: (" + aabb.Center.X + ", " + aabb.Center.Y + ", " + aabb.Center.Z + ")");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExpected: (" + cx + ", " + cy + ", " + cz + ")");
}
if (aabb.Extents.X != ex || aabb.Extents.Y != ey || aabb.Extents.Z != ez) {
System.Console.ForegroundColor = System.ConsoleColor.Red;
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB" + num + ", extents is wrong");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tGot: (" + aabb.Extents.X + ", " + aabb.Extents.Y + ", " +aabb.Extents.Z + ")");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExpected: (" + ex + ", " + ey + ", " + ez + ")");
}
}
protected void CheckAABBMinMax(AABB aabb, int num, float minX, float minY, float minz, float maxX, float maxY, float maxZ) {
Point t = aabb.Min;
if (t.X != minX || t.Y != minY || t.Z != minz) {
System.Console.ForegroundColor = System.ConsoleColor.Red;
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB" + num + ", min is wrong");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tGot: (" + t.X + ", " + t.Y + ", " + t.Z + ")");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExpected: (" + minX + ", " + minY + ", " + minz + ")");
}
t = aabb.Max;
if (t.X != maxX || t.Y != maxY || t.Z != maxZ) {
System.Console.ForegroundColor = System.ConsoleColor.Red;
System.Console.WriteLine("AABB" + num + ", max is wrong");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tGot: (" + t.X + ", " + t.Y + ", " + t.Z + ")");
System.Console.WriteLine("\tExpected: (" + maxX + ", " + maxY + ", " + maxZ + ")");
}
}
public override void Render() {
Vector3 eyePos = new Vector3();
eyePos.X = cameraAngle.Z * -(float)System.Math.Sin(cameraAngle.X * rads * (float)System.Math.Cos(cameraAngle.Y * rads));
eyePos.Y = cameraAngle.Z * -(float)System.Math.Sin(cameraAngle.Y * rads);
eyePos.Z = -cameraAngle.Z * (float)System.Math.Cos(cameraAngle.X * rads * (float)System.Math.Cos(cameraAngle.Y * rads));
Matrix4 lookAt = Matrix4.LookAt(eyePos, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), new Vector3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
GL.LoadMatrix(Matrix4.Transpose(lookAt).Matrix);
DrawAABBDebug(aabb1);
DrawAABBDebug(aabb2);
DrawAABBDebug(aabb3);
}
protected void DrawAABBDebug(AABB aabb) {
GL.Color3(1f, 1f, 1f);
aabb.Render();
GL.Color3(1f, 1f, 0f);
aabb.Min.Render();
GL.Color3(1f, 0f, 1f);
aabb.Max.Render();
GL.Begin(PrimitiveType.Lines);
GL.Color3(1f, 0f, 0f);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X, aabb.Center.Y, aabb.Center.Z);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X + aabb.Extents.X, aabb.Center.Y, aabb.Center.Z);
GL.Color3(0f, 1f, 0f);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X, aabb.Center.Y, aabb.Center.Z);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X, aabb.Center.Y + aabb.Extents.Y, aabb.Center.Z);
GL.Color3(0f, 0f, 1f);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X, aabb.Center.Y, aabb.Center.Z);
GL.Vertex3(aabb.Center.X, aabb.Center.Y, aabb.Center.Z + aabb.Extents.Z);
GL.End();
GL.Color3(0f, 1f, 1f);
aabb.Center.Render();
}
public override void Update(float deltaTime) {
cameraAngle.X += 45.0f * deltaTime;
}
public override void Resize(int width, int height) {
GL.Viewport(0, 0, width, height);
GL.MatrixMode(MatrixMode.Projection);
float aspect = (float)width / (float)height;
Matrix4 perspective = Matrix4.Perspective(60, aspect, 0.01f, 1000.0f);
GL.LoadMatrix(Matrix4.Transpose(perspective).Matrix);
GL.MatrixMode(MatrixMode.Modelview);
GL.LoadIdentity();
}
}
}